鱼类卵黄原蛋白(vitellogenin, Vtg)是国际上通用的环境雌激素生物标志物, 其测定通常采用酶联免疫吸附方法(ELISA)。Vtg在纯化和保存过程中容易发生降解[1], 会降低以Vtg抗原建立的ELISA的精确度, 从而给样品Vtg的定量结果造成误差[2-3]。最近, 有研究发现Vtg在卵巢中的主要酶解产物——卵黄脂磷蛋白(lipovitellin, Lv)非常稳定, 并且与Vtg具有相同的免疫原性, 以Lv代替Vtg用作抗原建立的ELISA能够更加准确地定量鱼类Vtg[4]。
鲫(Carassius carassius)是野外水体环境雌激素检测常用的受试鱼种[5-6]。鲫Vtg指标被广泛用于评价河流、湖泊和污水处理厂排水等多种水体的雌激素污染状况[7-9], 但是这些研究都是利用以Vtg为抗原建立的ELISA方法。为准确定量鲫Vtg, 本研究对鲫Lv进行了分离纯化与性质鉴定, 并利用本实验室制备的斑马鱼(Danio rerio) Lv抗体和金鱼(Carassius auratus) Lv抗体开发了2种ELISA方法, 以期建立高精确度的鲫Vtg检测方法。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验用鱼性成熟的鲫购自青岛市市南区水产市场, 体重(110±20) g, 体长(20±1) cm。经0.075 g/L的MS- 222麻醉后, 解剖, 取雌鱼卵巢, 用于Lv的纯化。
1.2 卵巢匀浆液的制备采用Hiramatsu等[10]的方法, 将5倍重量的匀浆液(20 mmol/L Tris-HCl, 10 mmol/L EDTA和100 mmol/L NaCl, pH 7.5)加入到卵巢中, 在冰浴条件下用玻璃匀浆器匀浆, 4℃, 10000 g离心15 min, 上清液用0.45 μm滤膜过滤后, 分装备用。
1.3 卵黄脂磷蛋白的纯化 1.3.1 纯化方案I:凝胶过滤结合离子交换层析按照单瑞后等[11]的方法将1 mL卵巢匀浆液进行凝胶过滤层析(Sephacryl S-300 HR 16/70; GE Healthcare, Uppsala, Sweden), 将可能含有Lv蛋白的洗脱液进行离子交换层析(DEAE-Sepharose F F 12/20; GE Healthcare)。用含有0.07 mol/L、0.1 mol/L、0.2 mol/L和1 mol/L NaCl的25 mmol/L Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH 7.5)依次进行洗脱, 收集洗脱液, 经Native-PAGE检测后, 保存于–80℃。
1.3.2 纯化方案II:选择性沉淀结合离子交换层析选择性沉淀法根据Norberg[12]的方法略作调整。向1 mL卵巢匀浆液中加入2 mL 20 mmol/L EDTA (pH 7.7)和0.1 mL 0.5 mol/L MgCl2, 随后用10 mL预冷的双蒸水稀释, 4000 g离心20 min, 取上清, 按照1.3.1的方法进行离子交换层析。
1.4 电泳和特异性染色Native-PAGE按照Davis[13]的方法, 制备4.0%的浓缩胶和7.5%的分离胶, 将10 μL样品缓冲液(0.20 mol/L Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 25%甘油, 0.1%溴酚兰)加入到等体积的样品中, 离心混匀后每孔上样10 μL, 电压150 V, 4℃电泳。电泳结束后, 将凝胶取下分别进行考马斯亮蓝、Schiff试剂[14]、甲基绿[15]和苏丹黑B[16]染色。
1.5 分子量的测定采用5%~9%的分离胶进行电泳测定Lv的天然分子量。标准蛋白(Amersham, Sweden)含有甲状腺蛋白(669 kD)、铁蛋白(440 kD)、过氧化氢酶(232 kD)、乳酸脱氢酶(140 kD)、牛血清蛋白(67 kD)。电泳结束后进行考马斯亮蓝染色, 根据郭尧君[17]的方法计量分子量。
SDS-PAGE按照Laemmli[18]的方法, 将等体积的SDS缓冲液(0.16 mol/L Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 25%甘油, 0.1%溴酚兰, 4% SDS, 5%巯基乙醇)加入到10 µL样品中, 煮沸6 min, 电压200 V, 室温下进行电泳, 电泳后用考马斯亮蓝染色。根据标准蛋白的分子量与相对迁移率的线性回归方程计算分子量, 蛋白标准品(Fermentas, UAB)由分子量为20~200 kD的12种高纯蛋白组成。
1.6 蛋白浓度测定将方案Ⅰ和方案Ⅱ纯化得到的蛋白溶液分别混合后, 利用Bradford法, 以牛血清蛋白(BSA)为标准品计算2种方法纯化的Lv浓度, 并根据它们各自的体积计算2种方法纯化的Lv总量。
1.7 Western blot按照Towbin等[19]的方法, 取10 μL纯化的鲫Lv与实验室此前纯化的金鱼Lv和斑马鱼Lv进行SDS-PAGE (4%~9%), 电泳结束后将蛋白质转印到PVDF膜上, 4℃封闭过夜后, 将2张PVDF膜分别使用1︰1000稀释的金鱼Lv抗体和斑马鱼Lv抗体室温孵育4 h, 再使用1︰2000稀释的辣根过氧化物酶标二抗, 室温孵育4 h后, 将PVDF膜放入新鲜配制的DAB底物显色液中, 待条带清晰时用蒸馏水终止反应。
1.8 ELISA的建立参照Mitsui等[20]的方法, 将金鱼Lv抗体和斑马鱼Lv抗体稀释至5 μg/mL后, 4℃包被过夜; 次日, 37℃封闭1 h; 加入1.95~2000 ng/mL的金鱼Lv、斑马鱼Lv和鲫Lv, 孵育1 h; 加入1︰10000倍稀释的HRP标记金鱼Lv抗体和斑马鱼Lv抗体, 37℃孵育1 h; 每孔加入100 μL TMB单组分显色液, 37℃显色10 min后, 加入100 μL 2mol/L H2SO4终止反应, 测定450 nm波长下的吸光值, 并根据Nilsen等[21]的方法计算2种ELISA的检出限。
2 结果与分析 2.1 鲫Lv的纯化 2.1.1 凝胶过滤结合离子交换层析结果凝胶过滤层析图谱显示, 鲫卵巢匀浆液出现2个洗脱峰, 经Native-PAGE检测, 第2个洗脱峰呈现清晰的蛋白条带(图 1), 收集该峰的洗脱组分进一步进行离子交换层析。
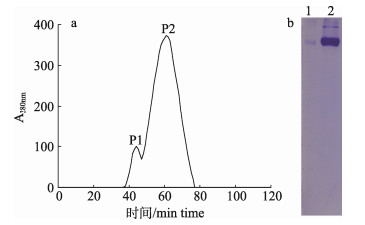
|
图 1 鲫卵匀浆液的凝胶过滤洗脱曲线(a)与Native-PAGE图谱(b) 1:峰1组分; 2:峰2组分. Fig.1 Elution curve of the egg homogenate of crucian carp on a Sephacryl S-300 gel filtration chromatography column 1: P1; 2: P2. |
离子交换层析结果显示, 在0.2 mol/L NaCl处出现了主洗脱峰, 并且该峰检测到一条蛋白条带(图 2)。该峰共收到了9.5 mL洗脱液, 经测定蛋白浓度为0.88 mg/mL, 总蛋白含量为8.36 mg。
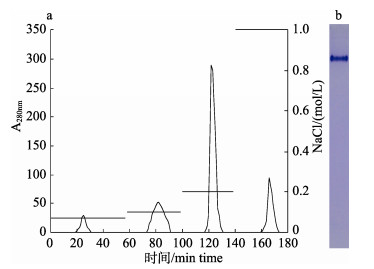
|
图 2 鲫卵匀浆液凝胶过滤结合离子交换层析洗脱曲线(a)与Native-PAGE图谱(b) Fig.2 Elution curve of the egg homogenate of crucian carp on DEAE anion exchange column (a) and native-PAGE analysis (b) |
将选择性沉淀后的上清进行离子交换层析, 在0.07 mol/L和0.2 mol/L NaCl处出现洗脱峰, 电泳结果显示0.2 mol/L NaCl洗脱组分呈现单一条带(图 3)。该峰收集了15.3 mL洗脱液, 经测定蛋白浓度为0.63 mg/mL, 总蛋白含量为9.64 mg。
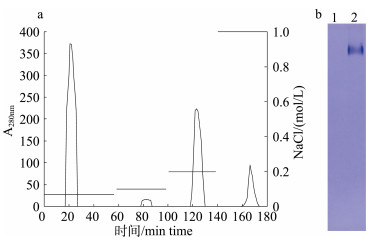
|
图 3 鲫卵匀浆液选择性沉淀后离子交换层析洗脱曲线(a)和Native-PAGE图谱(b) 1: 0.07 mol/L NaCl; 2: 0.2 mol/L NaCl. Fig.3 Elution curve of ion exchange chromatography after selective precipitation of the crucian carp egg homogenate (a) and native-PAGE analysis (b) Lane 1: 0.07 mol/L NaCl; lane 2: 0.2 mol/L NaCl. |
将纯化的蛋白进行Native-PAGE后, 分别用考马斯亮蓝、Schiff试剂、甲基绿、苏丹黑B染色, 结果显示该蛋白能同时被4种染色方法着色(图 4)。
|
图 4 鲫Lv的糖、磷、脂特异性染色
1.考马斯亮蓝染色; 2.脂蛋白染色; 3.糖蛋白染色; 4.磷蛋白染色. Fig.4 Determination of carbohydrate, lipid and phosphorus in the crucian carp Lv Lane 1: stained by CBB G250; lane 2: lipoprotein stained by Sudan black B; lane 3: glycoportein stained by Schiff reagent; 4: phosphoprotein stained by Methyl green. |
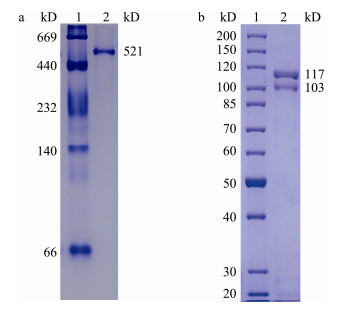
根据蛋白条带相对迁移率测得鲫Lv的天然分子量约为521 kD, 在SDS-PAGE中显示分子量分别为117 kD和103 kD的2条清晰条带与1条分子量约为75 kD的模糊条带(图 5)。
|
图 5 鲫Lv天然分子量(a)和变性条件分子量(b) 1:标准蛋白; 2:鲫Lv. Fig.5 Crucian carp Lv natural molecular weight (a) and denaturing conditions molecular weight (b) Lane 1: maker; lane 2: crucian carp Lv. |
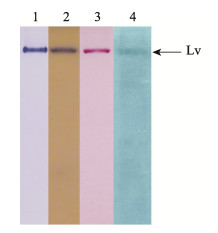
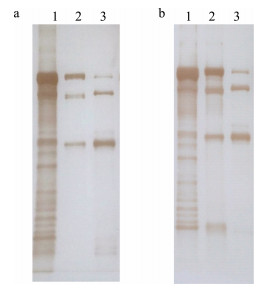
Western blot结果显示, 金鱼Lv抗体和斑马鱼Lv抗体都能与金鱼、斑马鱼和鲫的Lv发生反应, 其中金鱼Lv呈现多个条带, 斑马鱼和鲫Lv呈现3条清晰的条带(图 6)。
|
图 6 金鱼、斑马鱼和鲫Lv与金鱼Lv抗体(a)和斑马鱼Lv抗体(b)的Western blot结果
1:金鱼Lv, 2:斑马鱼Lv, 3:鲫Lv.
Fig.6 Western blot analysis of goldfish, zebrafish and crucian carp Lv detected by anti-goldfish Lv antibody (a) and anti-zebrafish Lv antibody (b)
Lane 1: goldfish Lv; lane 2: zebrafish Lv; lane 3: crucian carp Lv. |
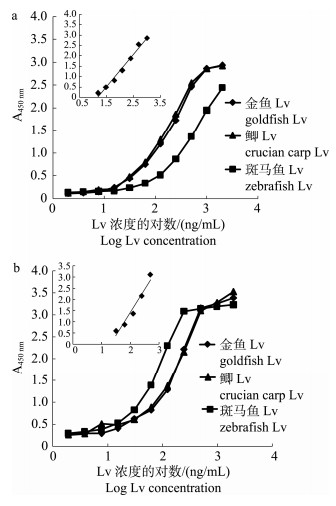
以金鱼Lv抗体为包被抗体、纯化的3种鱼类Lv为抗原, 以HRP标记的金鱼Lv抗体建立夹心ELISA(图 7a), 金鱼Lv和鲫Lv的结合曲线基本重合, 并且明显高于斑马鱼Lv的结合曲线(图 7a), 以鲫Lv为抗原的夹心ELISA工作范围为15.6~ 1000 ng/mL (Y=1.56X–1.83, R2=0.982), 检出限约为6.8 ng/mL。
|
图 7 金鱼、斑马鱼和鲫Lv在两种ELISA中的结合曲线 Fig.7 The binding curves of goldfish Lv, zebrafish Lv, and crucian carp Lv in two ELISA assays |
同样, 利用3种鱼类Lv与斑马鱼Lv抗体构建夹心ELISA, 金鱼Lv和鲫Lv的结合曲线也基本重合, 但是要低于斑马鱼Lv的结合曲线(图 7b)。夹心ELISA对鲫Lv的检测范围为31.2~500 ng/mL (Y=2.07X-2.73, R2=0.953), 检出限约为15.2 ng/mL。
3 讨论本研究利用纯化的鲫Lv建立夹心ELISA, 为鲫Vtg的准确定量提供了重要方法。鱼类Vtg与Lv的纯化通常采用凝胶过滤与离子交换相结合的两步层析法[22], 选择性沉淀结合离子交换层析的方法也被少数研究者用于Vtg的纯化[23]。本研究利用凝胶过滤结合离子交换层析(方案I)与选择性沉淀结合离子交换层析(方案II) 2种方案从鲫卵匀浆液中纯化Lv。2种方法纯化的蛋白在Native-PAGE中都显示单一条带, 特异性染色结果显示该蛋白为糖磷脂蛋白, 这符合鱼类Lv的基本特征[24-25]; 该蛋白的天然分子量约为521 kD, 结合SDS-PAGE测得了亚基分子量, 推测鲫Lv由2组分子量为117 kD和103 kD的亚基和1个分子量为75 kD的亚基组成的, 这与斑马鱼和金鱼等其他鲤科鱼类的Lv研究结果相近[25-26]。根据以上结果断定纯化的蛋白为鲫Lv。此外, 2种方案纯化得到的蛋白总量较为接近, 对Lv的纯化得率没有显著差别。与方案I相比, 方案II不需要凝胶过滤层析的装填、平衡以及洗脱等步骤, 大约可以节省近8 h, 可见选择性沉淀结合离子交换层析的方法更适合鱼类Lv的纯化。
Vtg或Lv抗体是建立Vtg ELISA的基础[27-28]。抗体的制备需要反复免疫动物、费时费力, 研究发现Vtg抗体能够识别同科鱼类的Vtg[21], 例如鲤(Cyprinus carpio) Vtg抗体常用于检测金鱼、斑马鱼等鲤科鱼类的Vtg[29-30]。王军[26]发现金鱼Lv抗体能有效检测斑马鱼、鲫、鲤、石鲽(Platichthys bicoloratus)、真鲷(Pagrosomus major)等多种鱼类的Vtg, 比Vtg抗体具有更广泛的应用范围。因此, 本研究尝试利用金鱼Lv抗体与斑马鱼Lv抗体建立鲫Vtg的夹心ELISA。在本研究中, Western blot结果显示金鱼Lv抗体和斑马鱼Lv抗体能检测到鲫、金鱼和斑马鱼Lv的多条清晰条带, 表明2种抗体都能和鲫Lv发生很好的交叉反应。相比之下, 斑马鱼Lv和鲫Lv显示3条条带, 而金鱼Lv出现了多条带, 这可能与金鱼Lv存放时间过长发生了部分降解有关。利用鲫Lv与金鱼和斑马鱼的Lv抗体建立了2种夹心ELISA, 其中基于金鱼Lv抗体建立的ELISA工作范围为15.6~1000 ng/mL, 检出限约为6.8 ng/mL, 显著低于李康等[31]建立的以鲫Vtg为抗原的竞争ELISA(工作范围为390~25000 ng/mL), 以及此前研究者开发的鲤和日本青鳉(Oryzias latipes)的Vtg ELISA[32-33]。与竞争ELISA相比, 夹心ELISA是通过包被的抗体直接捕获抗原, 随后HRP标记抗体与捕获抗原的结合起到信号放大作用, 因此本研究建立的夹心ELISA具有更高的敏感度。金鱼是由鲫进化而来的, 两者在蛋白水平上具有很高的同源性[34], 推测这可能是基于金鱼Lv抗体ELISA对鲫Lv的检测敏感度高于斑马鱼Lv抗体ELISA的主要原因。Wang等[35-36]发现在Lv抗体建立的ELISA中, 斑马鱼和金鱼的Lv标准曲线都与Vtg的标准曲线基本重合, 证实以Lv与Lv抗体建立的ELISA能够用于Vtg的定量。因此, 本研究利用鲫Lv与金鱼Lv抗体开发的夹心ELISA可以准确定量鲫Vtg, 为鲫Vtg的检测提供了可靠方法。
| [1] |
Magalhães I, Ledrich M L, Pihan J C, et al. One-step, non-denaturing purification method of carp (Cyprinus carpio) vitellogenin[J]. Journal of Chromatography B Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical & Life Sciences, 2004, 799(1): 87-93. |
| [2] |
Arukwe A, Goks yr A. Eggshell and egg yolk proteins in fish: hepatic proteins for the next generation: oogenetic, population, and evolutionary implications of endocrine disruption[J]. Comparative Hepatology, 2003, 2(1): 4. DOI:10.1186/1476-5926-2-4 |
| [3] |
Brodeur J C, Woodburn K B, Zhang F, et al. Plasma sampling and freezing procedures influence vitellogenin measurements by enzyme-linked immunoassay in the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas)[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2006, 25(2): 337-348. DOI:10.1897/05-368R.1 |
| [4] |
Wang J, Shan R, Zhang X, et al. Development of a lipovitellin-based sandwich ELISA for quantification of vitellogenin in surface mucus and plasma of goldfish (Carassius auratus)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 120: 80-87. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.05.010 |
| [5] |
Lu G H, Song W T, Wang C, et al. Assessment of in vivo estrogenic response and the identification of environmental estrogens in the Yangtze River (Nanjing section)[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 80(9): 982-990. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.05.038 |
| [6] |
Song W T, Lu G H, Wang C, et al. Study on environmental estrogen pollution in Yangtze River (Nanjing section) by an in vivo bioassay[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2010, 84(4): 406-412. DOI:10.1007/s00128-010-9944-9 |
| [7] |
Shao J, Shi G, Jin X, et al. Preliminary survey of estrogenic activity in part of waters in Haihe River, Tianjin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(22): 2565-2570. DOI:10.1007/BF03183651 |
| [8] |
Liu J, Wang R, Huang B, et al. Biological effects and bioaccumulation of steroidal and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in high-back crucian carp exposed to wastewater treatment plant effluents[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 162: 325-331. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2011.11.036 |
| [9] |
Wang R H, Liu J, Yang X, et al. Biological response of high-back crucian carp (Carassius auratus) during different life stages to wastewater treatment plant effluent[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013, 20(12): 8612-8620. DOI:10.1007/s11356-013-1817-4 |
| [10] |
Hiramatsu N, Hara A. Relationship between vitellogenin and its related egg yolk proteins in Sakhalin taimen (Hucho perryi)[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology, 1996, 115(3): 243-251. DOI:10.1016/0300-9629(96)00055-2 |
| [11] |
Shan R H, Wang S, Wang J, et al. Purification and characterization identification of lipovitellin from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2015, 22(4): 638-644. [单瑞后, 王松, 王骏, 等. 尼罗罗非鱼卵黄脂磷蛋白的分离纯化与性质鉴定[J]. 中国水产科学, 2015, 22(4): 638-644.] |
| [12] |
Norberg B. Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) vitellogenin: induction, isolation and partial characterization[J]. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 1995, 14(1): 1-13. DOI:10.1007/BF00004286 |
| [13] |
Davis B J. Disc elecrophoresis-Ⅱ. Method and application to human serum proteins[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1964, 121: 404-427. |
| [14] |
Fairbanks G, Steck T L, Wallach D F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane[J]. Biochemistry, 1971, 10(13): 2606-2617. DOI:10.1021/bi00789a030 |
| [15] |
Cutting J A, Roth T F. Staining of phospho-proteins on acrylamide gel electropherograms[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1973, 54(2): 386-394. DOI:10.1016/0003-2697(73)90367-9 |
| [16] |
Prat J P, Lamy J N, Weill J D. Staining of lipoproteins after electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel[J]. Bulletin de la Société de chimie biologique, 1969, 51(9): 1367. |
| [17] |
Guo Y J. Protein Electrophoresis Experiment Technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1999. [郭尧君. 蛋白质电泳实验技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999.]
|
| [18] |
Laemmli U K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4[J]. Nature, 1970, 227(5259): 680-685. DOI:10.1038/227680a0 |
| [19] |
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1979, 76(9): 4350-4354. DOI:10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350 |
| [20] |
Mitsui N, Tooi O, Kawahara A. Sandwich ELISAs for quantification of Xenopus laevis vitellogenin and albumin and their application to measurement of estradiol-17 beta effects on whole animals and primary-cultured hepatocytes[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2003, 135C(3): 305-313. |
| [21] |
Nilsen B M, Berg K, Eidem J K, et al. Development of quantitative vitellogenin-ELISAs for fish test species used in endocrine disruptor screening[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2004, 378(3): 621-633. DOI:10.1007/s00216-003-2241-2 |
| [22] |
Maltais D, Roy R L, Couillard C M. Hybrid ELISAs for vitellogenins of the endangered copper redhorse Moxostoma hubbsi and the shorthead redhorse Moxostoma macrolepidotum (Cypriniformes, catostomidae)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2010, 73(5): 883-892. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.03.005 |
| [23] |
Garnayak S K, Mohanty J, Rao T V, et al. Vitellogenin in Asian catfish, Clarias batrachus: Purification, partial characterization and quantification during the reproductive cycle by ELISA[J]. Aquaculture, 2013, 392: 148-155. |
| [24] |
Hara A, Yamauchi K, Hirai H. Studies on female-specific serum protein (vitellogenin) and egg yolk protein in Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) Studies on female-specific serum p[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Comparative Biochemistry, 1980, 65(2): 315-320. DOI:10.1016/0305-0491(80)90019-X |
| [25] |
Wiley H S, Wallace R A. The structure of vitellogenin. Multiple vitellogenins in Xenopus laevis give rise to multiple forms of the yolk proteins[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1981, 256(16): 8626-8634. |
| [26] |
Wang J. Purification and characterization identification of lipovitellin from Carassius auratus and preparation of polyclonal antisera[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [王军.金鱼卵黄脂磷蛋白的分离纯化、性质鉴定及其多克隆抗血清的制备[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.]
|
| [27] |
Holbech H, Andersen L, Petersen G I, et al. Development of an ELISA for vitellogenin in whole body homogenate of zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2001, 130(1): 119-131. |
| [28] |
Fujiwara Y, Fukada H, Shimizu M, et al. Purification of two lipovitellins and development of immunoassays for two forms of their precursors (vitellogenins) in medaka (Oryzias latipes)[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2005, 143(3): 267-277. DOI:10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.03.014 |
| [29] |
Tyler C R, van der Eerden B, Jobling S, et al. Measurement of vitellogenin, a biomarker for exposure to oestrogenic chemicals, in a wide variety of cyprinid fish[J]. Journal of Comparative Physiology B: Biochemical, Systemic, and Environmental Physiology, 1996, 166(7): 418-426. DOI:10.1007/BF02337886 |
| [30] |
Maltais D, Roy R L. A lateral flow immunoassay for rapid evaluation of vitellogenin levels in plasma and surface mucus of the copper redhorse (Moxostoma hubbsi)[J]. Enviro n mental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2007, 26(8): 1672-1676. DOI:10.1897/06-481R.1 |
| [31] |
Li K, Zhou Z L, Yu J, et al. Development of ELISA for detecting Carassius auratus vitellogenin[J]. China Environmental Science, 2003, 23(3): 276-280. [李康, 周忠良, 于静, 等. 鲫鱼(Carassius auratus)卵黄蛋白原的ELISA检测[J]. 中国环境科学, 2003, 23(3): 276-280. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2003.03.013] |
| [32] |
Hennies M, Wiesmann M, Allner B, et al. Vitellogenin in carp (Cyprinus carpio) and perch (Perca fluviatilis): purification, characterization and development of an ELISA for the detection of estrogenic effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2003, 309(1-3): 93-103. DOI:10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00005-6 |
| [33] |
Kordes C, Rieber E P, Gutzeit H O. An in vitro vitellogenin bioassay for oestrogenic substances in the medaka (Oryzias latipes)[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2002, 58(3-4): 151-164. DOI:10.1016/S0166-445X(01)00227-2 |
| [34] |
Zhuang Y H, Zhou Y, Niu Y D, et al. Molecular phylogenetic relationships of different varieties of goldfishes (Carssius auratus Var) and crucian carps (Carssius auratus)[J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2009, 18(1): 46-49. [庄远红, 周毅, 牛艳东, 等. 不同品种金鱼和鲫鱼的分子系统发育关系研究[J]. 激光生物学报, 2009, 18(1): 46-49. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2009.01.009] |
| [35] |
Wang J, Zhang X, Shan R, et al. Lipovitellin as an antigen to improve the precision of sandwich ELISA for quantifying zebrafish (Danio rerio) vitellogenin[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2016, 185-186: 87-93. |
| [36] |
Wang J, Shan R, Zhang X, et al. Development of a lipovitellin-based sandwich ELISA for quantification of vitellogenin in surface mucus and plasma of goldfish (Carassius auratus)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 120: 80-87. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.05.010 |
 2018, Vol. 25
2018, Vol. 25

